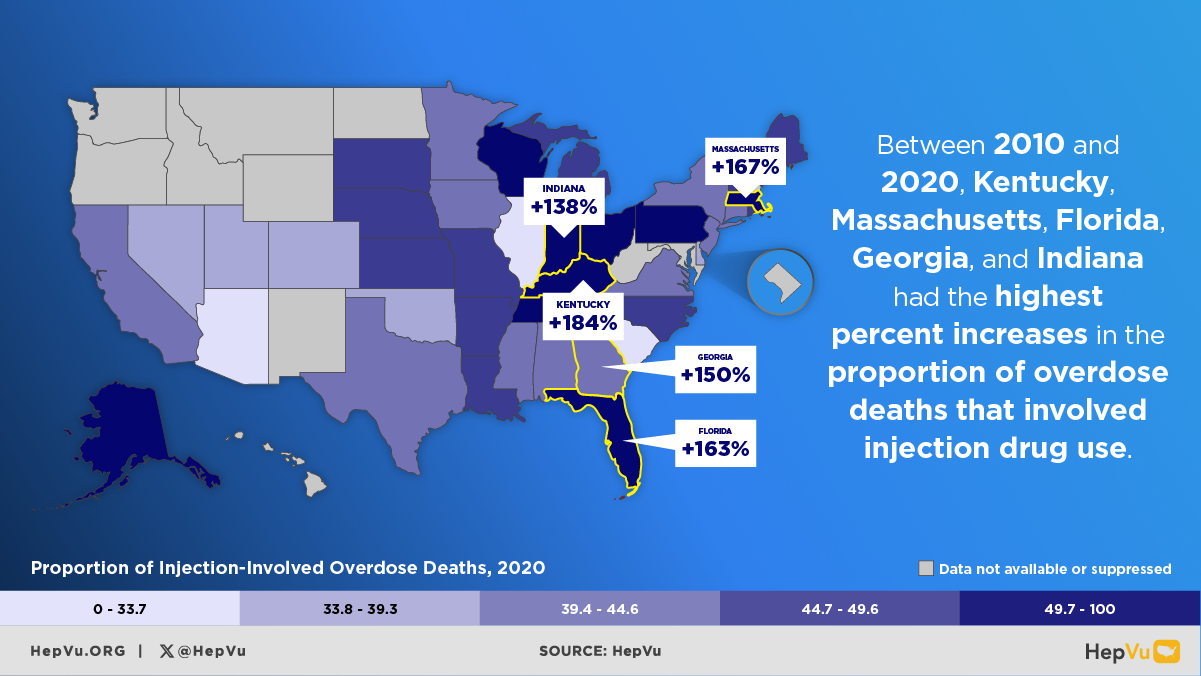
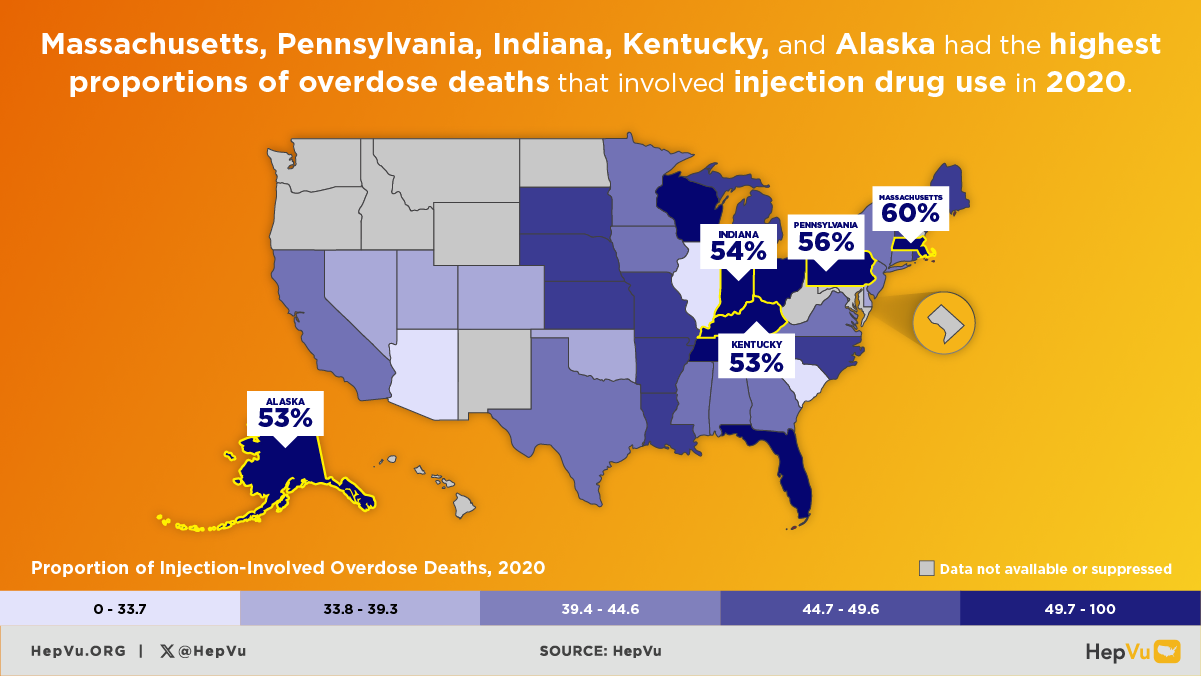
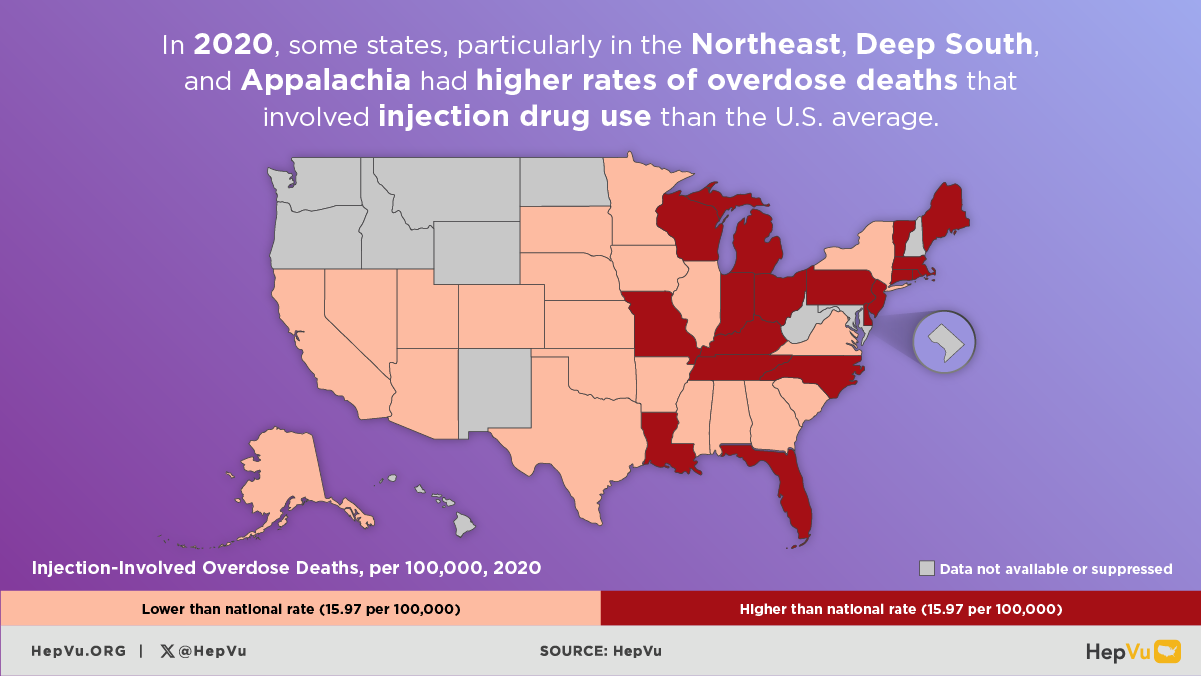
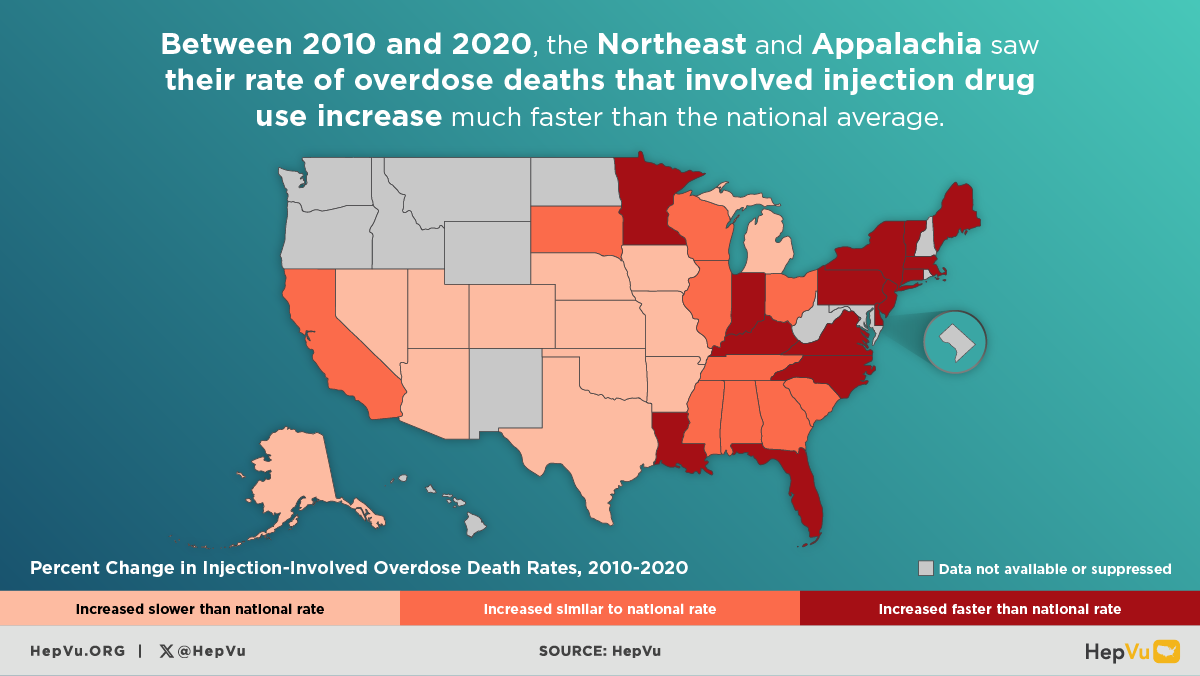
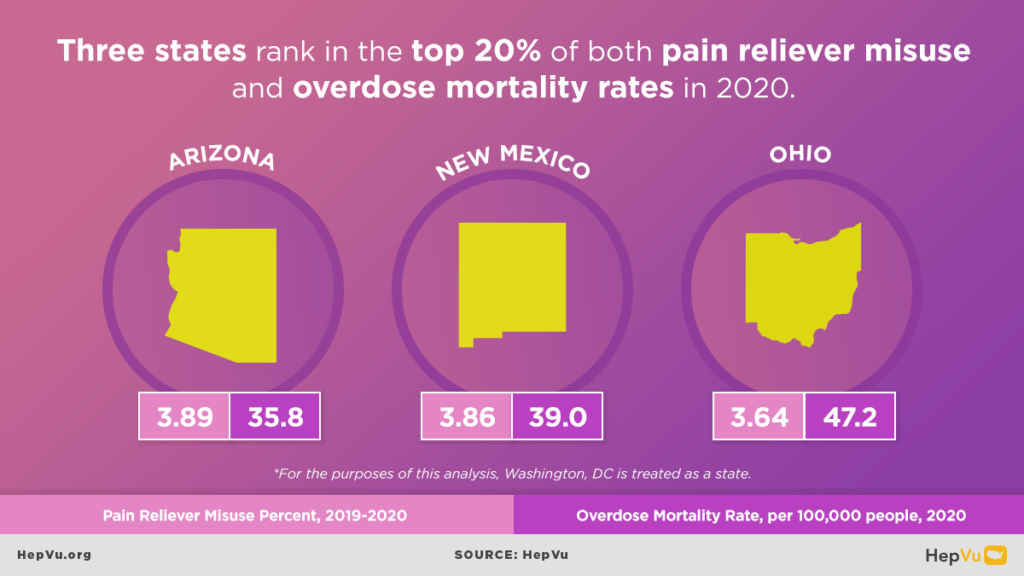
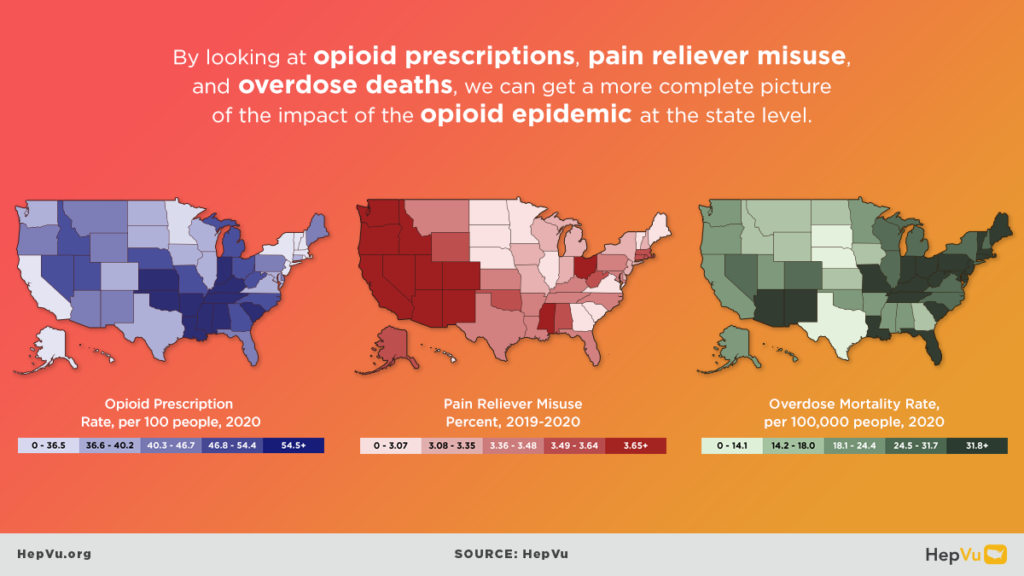
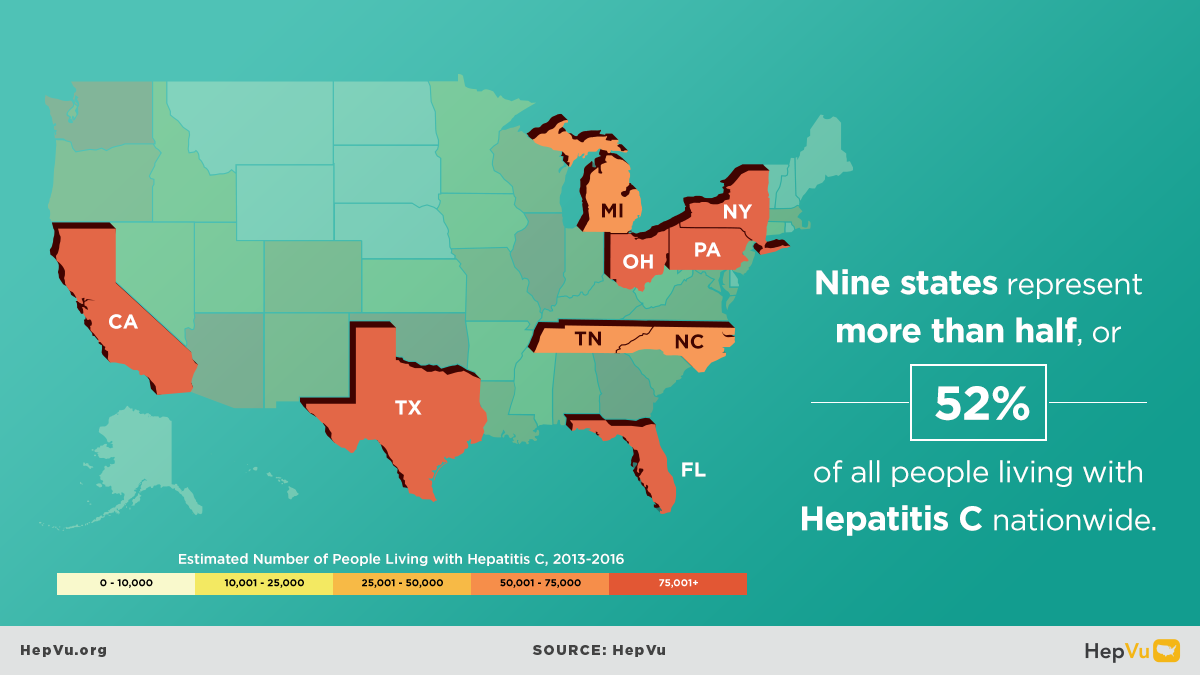
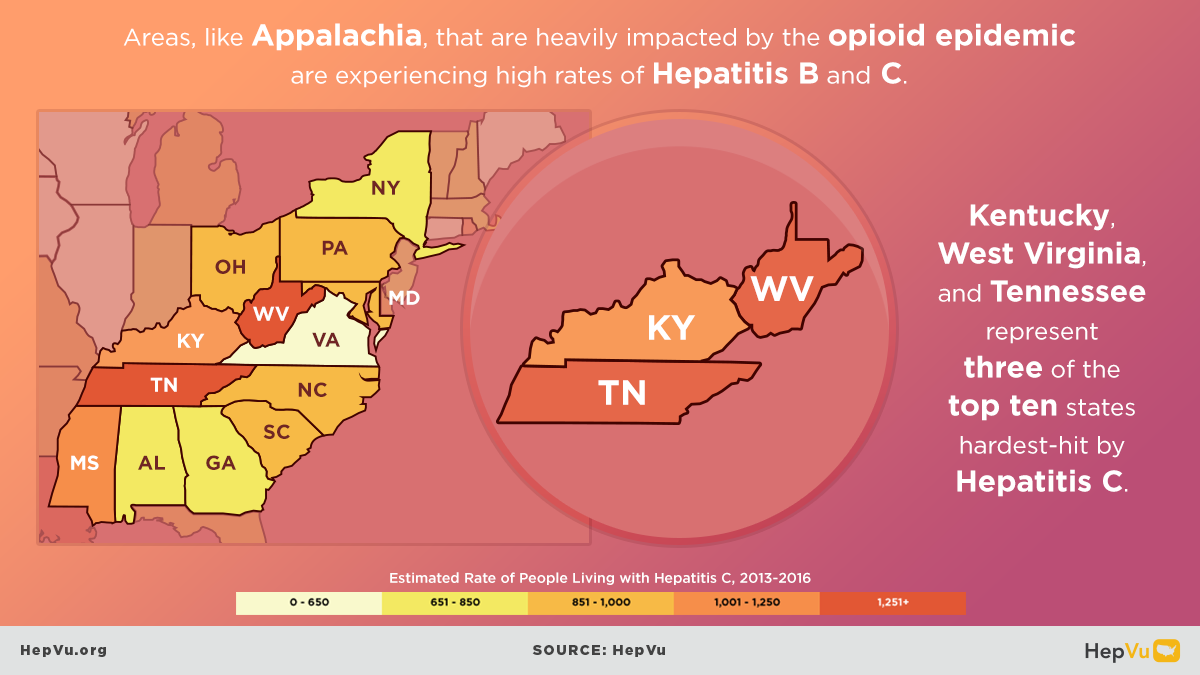
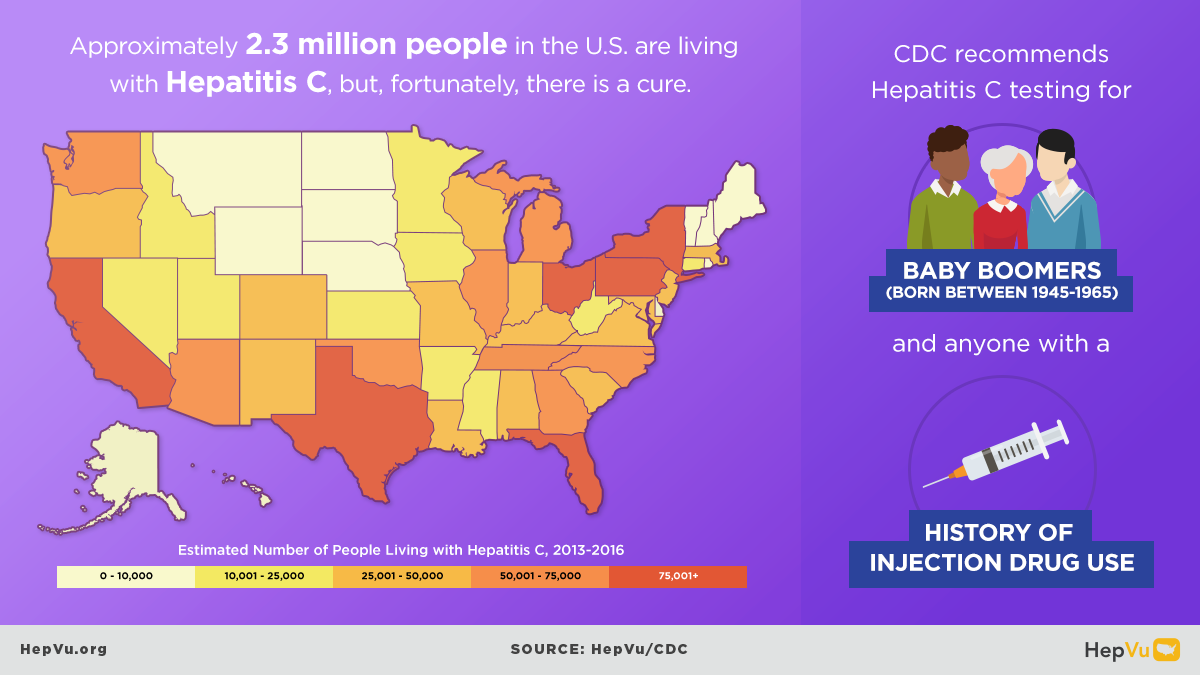
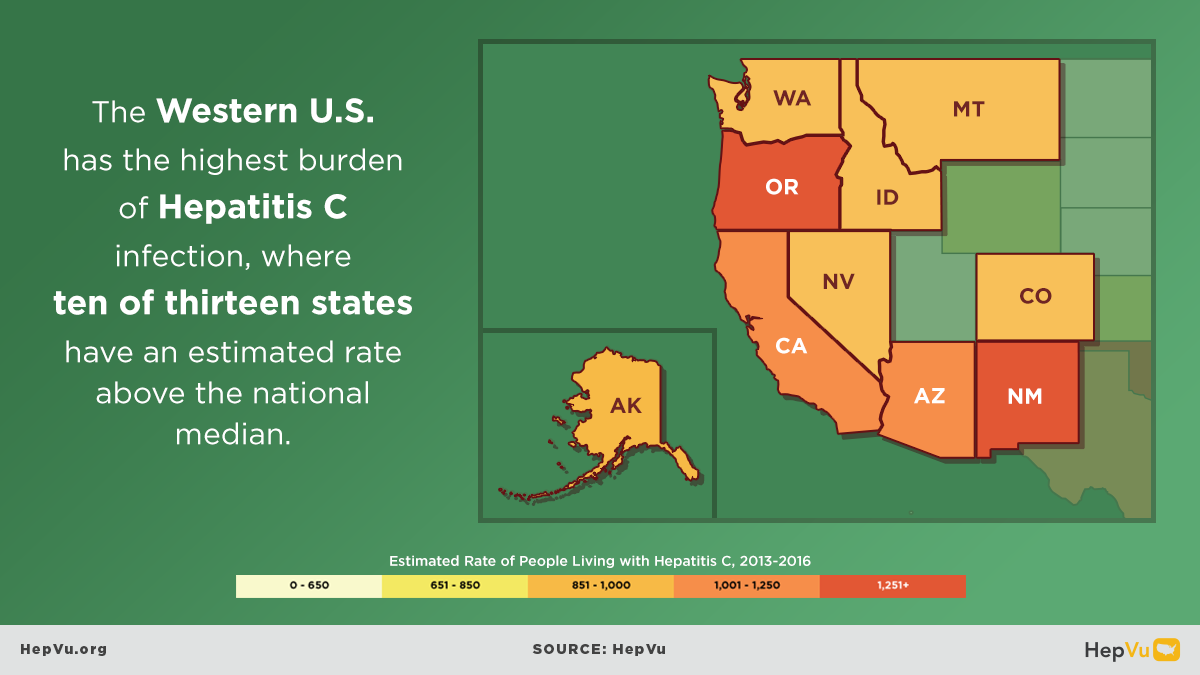
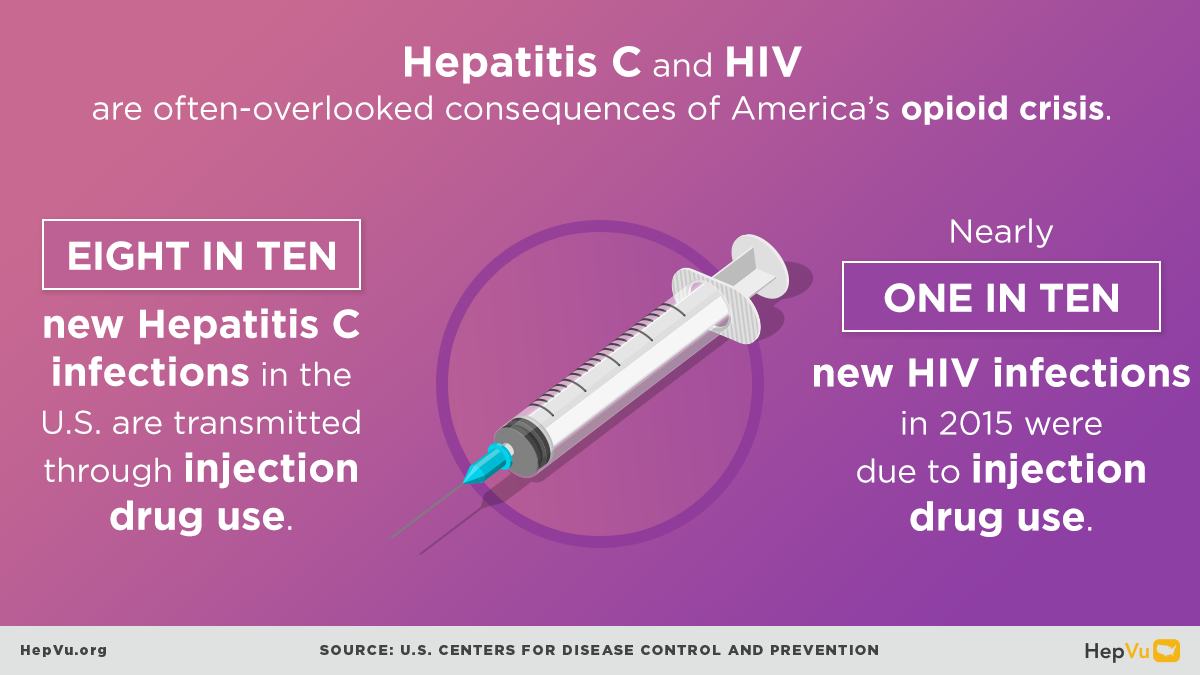
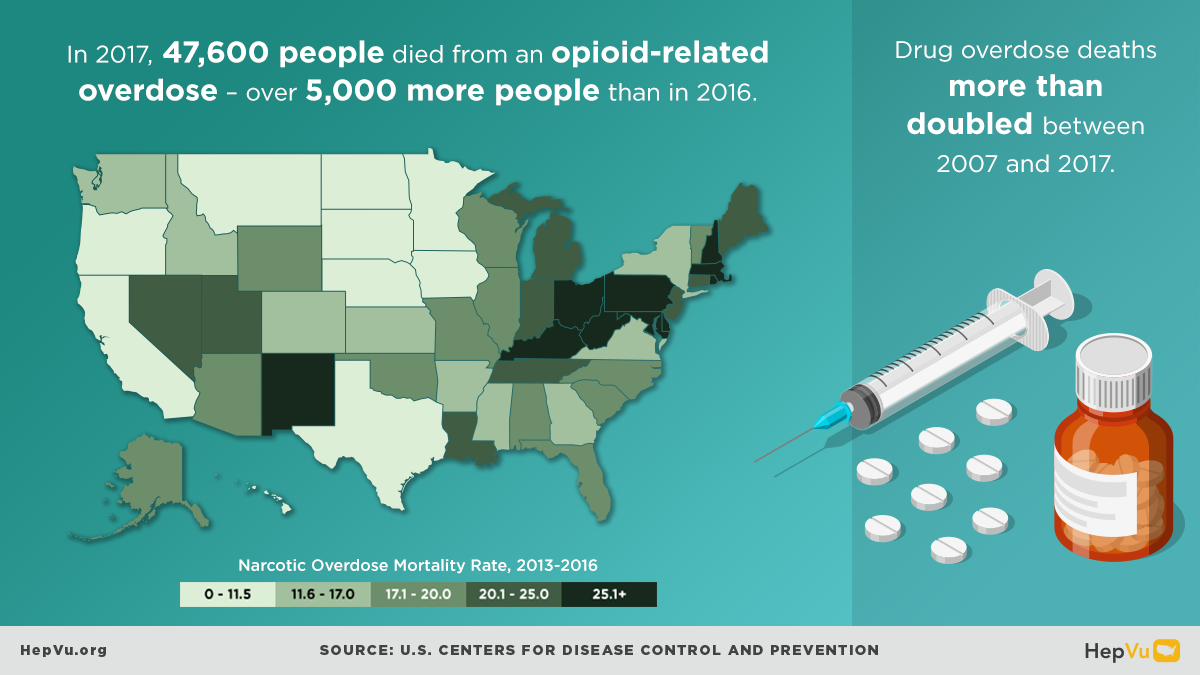
The opioid crisis is one of the greatest public health challenges facing the U.S., causing an unprecedented surge in overdose deaths, and fueling the rapid rise in new Hepatitis C infections from injection drug use in communities across the country. As opioid abuse rates have skyrocketed, new Hepatitis C infections have also increased. As many as 4 million Americans are living with Hepatitis C.
The Opioid Epidemic
In 2017, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) declared a public health state of emergency due to the opioid epidemic. Opioids are highly addictive and include prescription pain relievers, synthetic compounds such as fentanyl, and illegal drugs such as heroin. Nearly 108,000 persons in the U.S. died from drug-involved overdose in 2022, including illicit drugs and prescription opioids. Opioid-involved overdose deaths rose from 49,860 in 2019 to 81,806 in 2022. The opioid epidemic’s growth even contributed to a 0.67 year decrease in annual U.S. life expectancy between 2019 and 2022. Though these declines coincide with the period of the COVID-19 pandemic, opioid overdose deaths are an important contributor to decreasing US life expectancy. From November 2023 to October 2024, 78,378 United States residents died from an unintentional or undetermined intent drug overdose.
Key Insights:
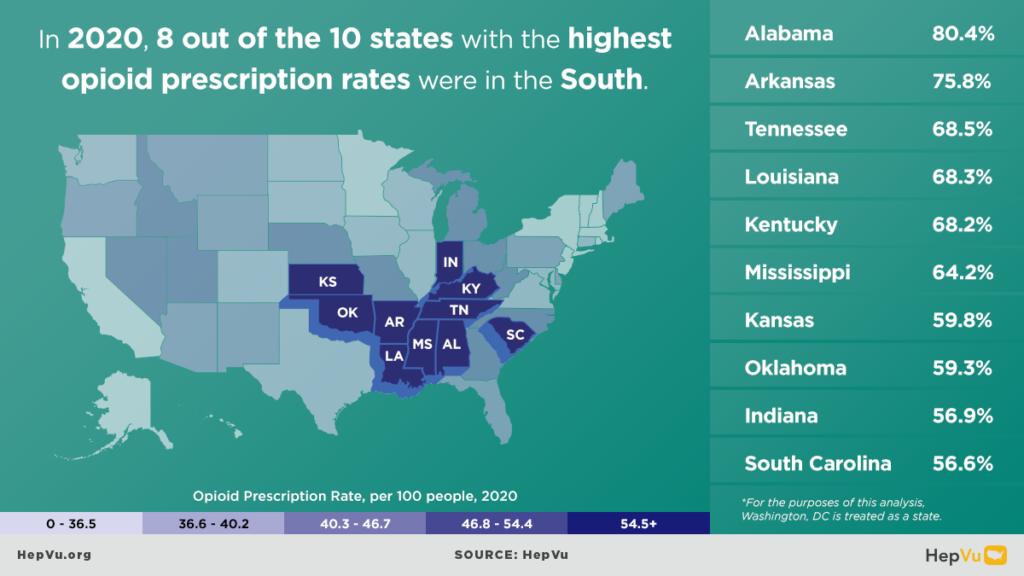
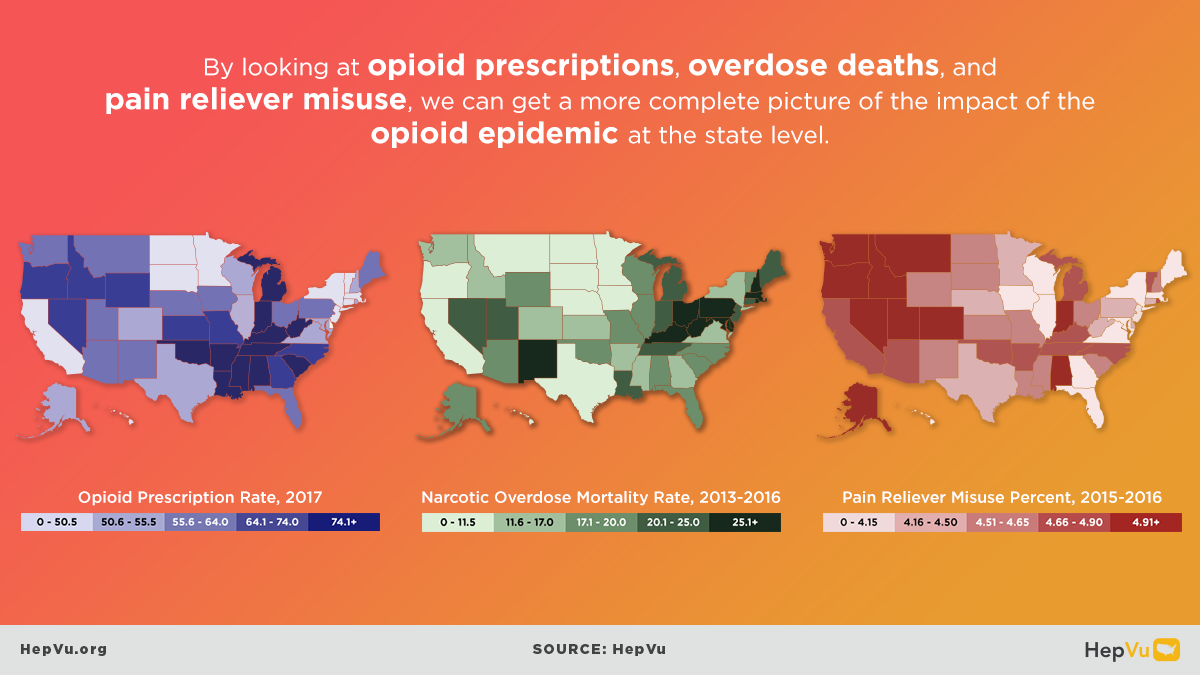
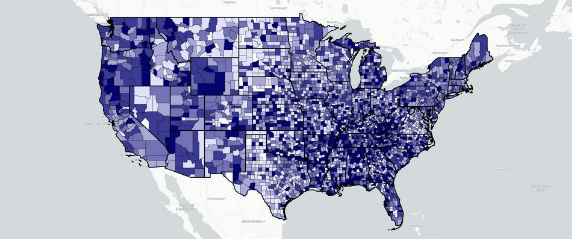
- In 2022, 8 of the top 10 states with the highest opioid dispensing rates were in the South.
- In 2022, 8 of the top 10 counties with the highest opioid dispensing rates across the U.S. were in either Virginia or Kentucky.
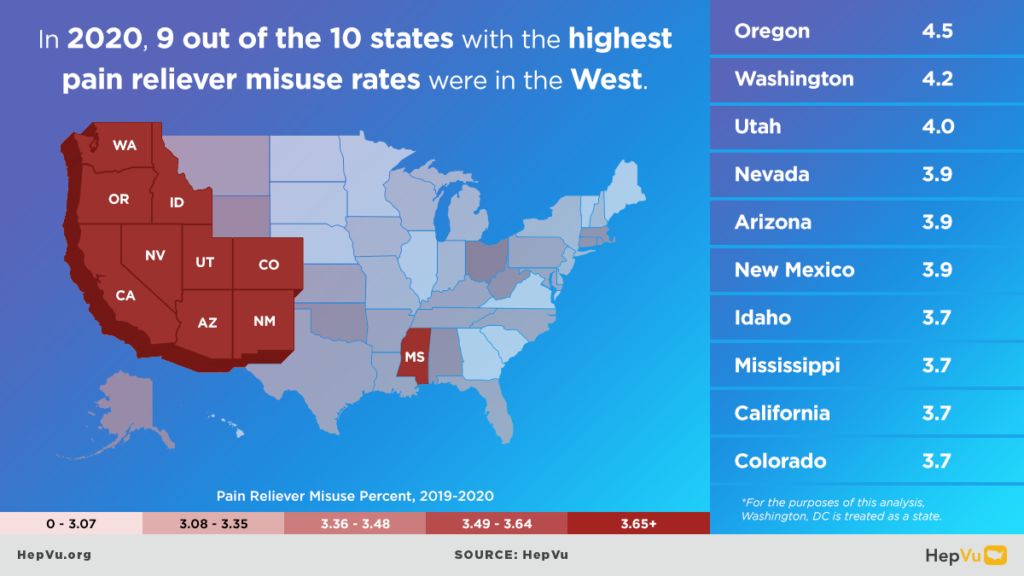
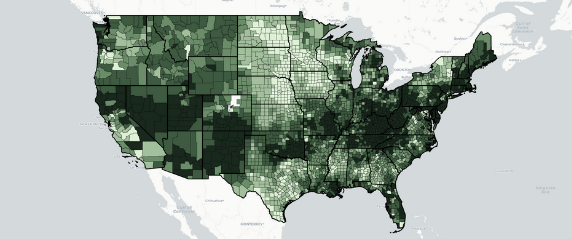
- In 2022, 6 of the top 10 states with the highest percentages of pain reliever misuse were in the South.
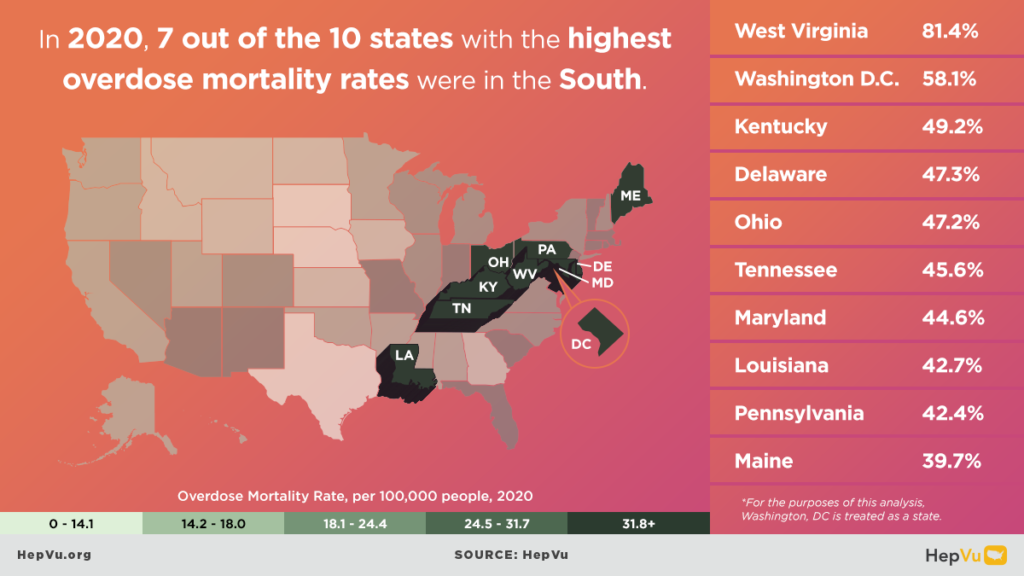
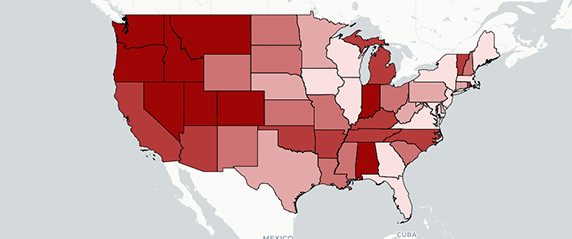
- In 2022, 7 of the top 10 states with the highest rates of narcotic overdose deaths were in the South.
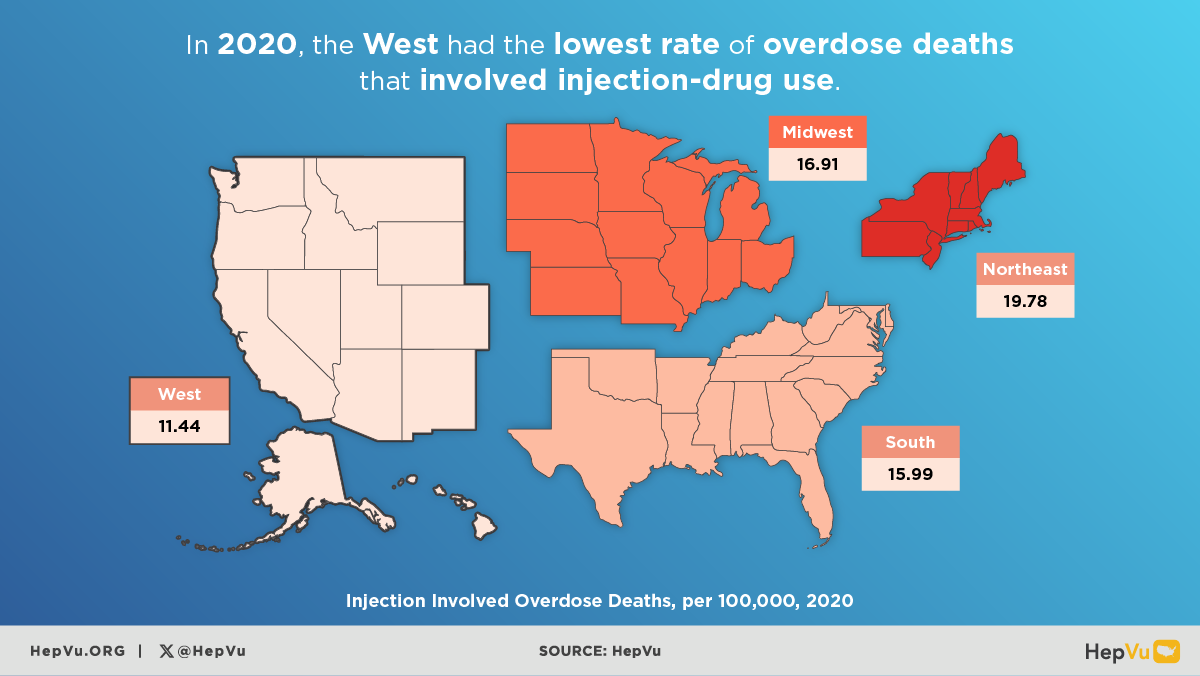
- In 2022, the Northeast region had the highest narcotic overdose mortality rate compared to other U.S. regions.
- In 2022, all top 10 states with the highest rates of Hepatitis C mortality are either in the South or West.
- North Dakota, Delaware, and South Dakota experienced more than a 30% increase in Hepatitis C mortality from 2021 to 2022.
The HIV and Hepatitis C Syndemic
A syndemic refers to two or more interrelated epidemics that are mutually reinforcing and interact in a way that amplifies the overall burden of disease. Although not all people who abuse opioids inject drugs, people who inject drugs are at significantly higher risk of transmission of blood-borne viruses, including HIV and Hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C and HIV can be transmitted by sharing needles, syringes, and other equipment used to inject drugs. In 62-80% of people who inject drugs co-infection with HIV and Hepatitis C is common. As younger Americans engage in injection drug use, there is also a greater risk of women of childbearing age contracting Hepatitis C as well as mother-to-child transmission.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends routine periodic HIV and viral hepatitis screening for people who inject drugs. Additionally, prevention efforts, such as syringe service programs and substance use treatment services, can slow the growth in the number of new Hepatitis C and HIV infections due to injection drug use. By identifying new infections early, patients can be treated for HIV, or cured of Hepatitis C, and stop additional infections from occurring.
People with HIV and Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and HIV are bloodborne viruses transmitted primarily through sexual contact and injection-drug use. Because of these shared modes of transmission, a high proportion of adults at risk for HIV infection are also at risk for HBV infection. People with HIV who become infected with HBV are at increased risk for liver-related morbidity and mortality.
4 Ways to Use HepVu
Explore Interactive Maps
View Local Statistics
View local statistics for your state, and download high-impact data visualizations for your work
See the Data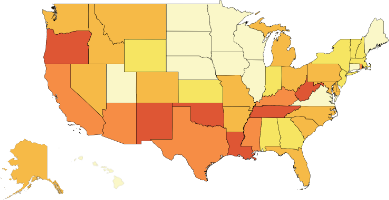
Download Data
See the DataLearn From Experts
Experts weigh in on the opioid epidemic and the resulting syndemic in HepVu’s blog series.

August 23, 2021
Dr. Eric Hall on County-Level Opioid Prescribing and Overdose Mortality Rates
Eric Hall, PhD, MPH, is a Postdoctoral Researcher for the Department of Epidemiology at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health. Q: Your research focuses on county-level overdose mortality and opioid prescription rates. Can you explain what these rates mean and how they relate to the viral hepatitis epidemic in the U.S.? Over the
Read More
March 25, 2021
Dr. Gregory Dore on Hepatitis C Treatment Barriers Among People Who Inject Drugs
Gregory Dore, MD is a Scientia Professor and the Head of Viral Hepatitis Clinical Research Program at the Kirby Institute at the University of New South Wales Sydney in Australia. Q: Your career focuses on Hepatitis C and other infectious diseases, especially among marginalized populations such as people who use drugs and people who experience homelessness.
Read More
March 18, 2021
Injection Drug Use and Hepatitis C Trends in the Indian Health Service
Richard Haverkate, MPH, is the National HIV/HCV Program Coordinator for the Indian Health Service. Q: In July 2020, you co-authored a study that analyzed trends in indicators of injection drug use (IDU) using data from the Indian Health Service inpatient and outpatient database from 2010-2014. What specific indicators did you select as proxies for injection drug use, and
Read More
April 21, 2020
Vu Q&A: Dr. Elinore McCance-Katz on Opioid Use Disorder
Elinore McCance-Katz, MD, PhD, is the first assistant secretary for mental health and substance use and leads the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Q: In 2017, you were nominated as the first Assistant Secretary for Mental Health and Substance Use and now lead the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
Read More
January 15, 2019
Vu Q&A: The Opioid Epidemic’s Impact on Hepatitis C in the U.S.
Heather Bradley, Ph.D., is an Assistant Professor of Epidemiology at Georgia State University and serves as HepVu Project Director. Ron Valdiserri, M.D., MPH, is Senior Research Associate and Distinguished Scholar, Johns Hopkins University, Bloomberg School of Public Health, Former Deputy Assistant Secretary for Health, Infectious Diseases, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, and serves
Read More
May 29, 2018
Vu Q&A: The Opioid Epidemic and Viral Hepatitis in Appalachia
Judith Feinberg has a joint appointment in the West Virginia University School of Medicine as a professor of Behavioral Medicine & Psychiatry and Medicine/Infectious Diseases. She is the Vice Chair of the HIV Medicine Association and a nationally-recognized expert on the opioid epidemic in West Virginia, Appalachia and rural America. Q: The number of new
Read More
January 10, 2018
Addressing Increases in Hepatitis C Infections Linked to the Opioid Epidemic
The other important component of the U.S. Hepatitis C epidemic is smaller in absolute numbers but is the major source of new Hepatitis C infections: infections associated with the opioid epidemic, injection drug use, and the sharing of needles and other drug injection equipment.
Read MoreFor More Information
Additional information about the opioid and Hepatitis C epidemics can be found at the following resources.
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Opioid Overdose: Understanding the Epidemic
Learn MoreU.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Increase in hepatitis C infections linked to worsening opioid crisis
Learn MoreSurgeon General
Facing Addition in America: The Surgeon General’s Spotlight on Opioids (PDF)
Learn More